Their is a great degree of confusion as regarding individuals who should be screened for gluten sensitivity/intolerance?
Their is a great degree of confusion as regarding individuals who should be screened for gluten sensitivity/intolerance?
Because research has shown that as many as 40% of all Americans may be gluten sensitive, and that 1 in 100 have a severe form of this sensitivity causing the the autoimmune intestinal disease, celiac sprue, a case can be made that everyone in America should be screened for gluten sensitivity.
However, there are people with various risk factors or diseases that are at greater risk of having gluten sensitivity who should undoubtedly be tested.
These conditions include:
• Microscopic colitis (inflammation of the colon)
• Relatives of those with celiac disease or gluten-sensitive individuals including
• Chronic diarrhea of unknown origin
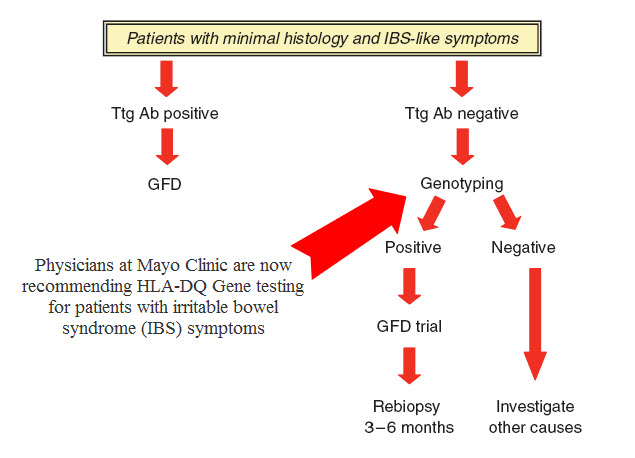
• Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
• Inflammatory bowel disease
• Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
• Hepatitis C
• Liver disease of unknown origin
• Dermatitis herpetiformis
• Diabetes mellitus
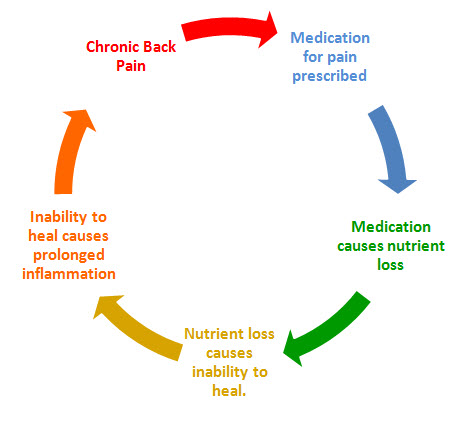
• Degenerative disc disease
• Colon Cancer
• Thyroid disease
• Psoriasis
• Any autoimmune diseases (common ones include):
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Sjogren’s syndrome
- Scleroderma
- Dermatomyositis
• Chronic Fatigue and Fibromyalgia
• PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome)
• Asthma
• Migraine Headaches
• Osteoporosis
• Iron deficiency
• Failure to thrive (FTT) or short stature in children
• Down’s syndrome
• Mothers of kids with neural tube defects
• Female infertility (includes those with multiple miscarriages)
• Peripheral neuropathy
• Cerebellar ataxia (unexplained dizziness)
• Seizure disorders
• Psychiatric disorders (Schizophrenia and bipolar)
• Depression
• Alcoholism
• Autism
• ADHD/ADD